This section covers the hopping of battery-powered devices. For a guide on how to hop mains-powered devices, see Hopping Mains-powered Devices.
Unlike WEMS devices such as the WEMScontroller1 and WEMScontroller4, WEMSsensors cannot 'listen' for incoming instructions from the WEMSprogrammer 24/7 as this would significantly reduce the life expectancy of their batteries. As such, any instructions or requests the WEMSprogrammer needs to send to a WEMSsensor need to be queued until the WEMSsensor initiates communications to the WEMSprogrammer. Once initiated the WEMSprogrammer can then keep the communication link open and send the information request/instruction.
From this there are two main points to consider when hopping battery-powered devices, the first is that updating the battery-powered devices could take up to 30 minutes as the WEMSprogrammer needs to wait for the WEMSsensor to initiate communications before the new hopping route can be given (and the standard heartbeat period for WEMSsensors is 30 minutes). The second important point to note is that because the WEMSsensor cannot listen for new instructions all the time, it cannot accept instructions from any device that is not currently in its hopping route – so a WEMSsensor needs to be able to communicate to the WEMSprogrammer via its current hopping route before new hopping instructions can be given.
To hop WEMSsensors in a trouble-free manner, please follow these steps:
- Take the WEMSsensor within reliable communication distance of the WEMSprogrammer and press the button 3–4 times; this will allow the system to discharge any pending info requests/instructions before the new hopping information is sent.
- Now disconnect the battery and take the WEMSsensor to a place where it will be able to communicate to the WEMSprogrammer AND the 1st device you wish the WEMSsensor to hop1 through.
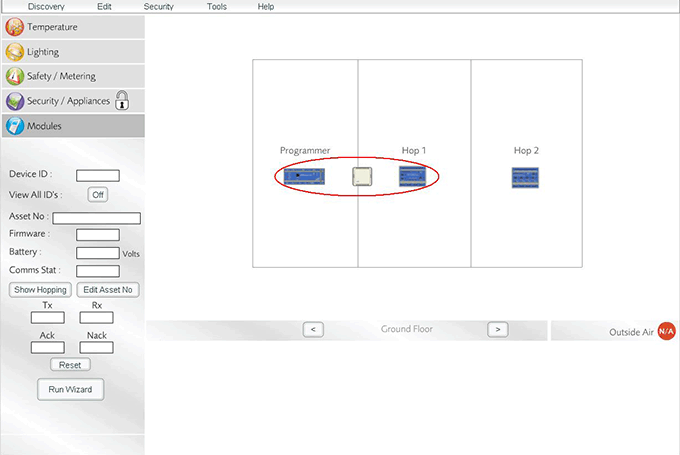
WEMSsensor within communication distance of both WEMSprogrammer and hop1 device.
- Open the hopping application via the menu and apply your ‘hop1’ route to the WEMSsensor.
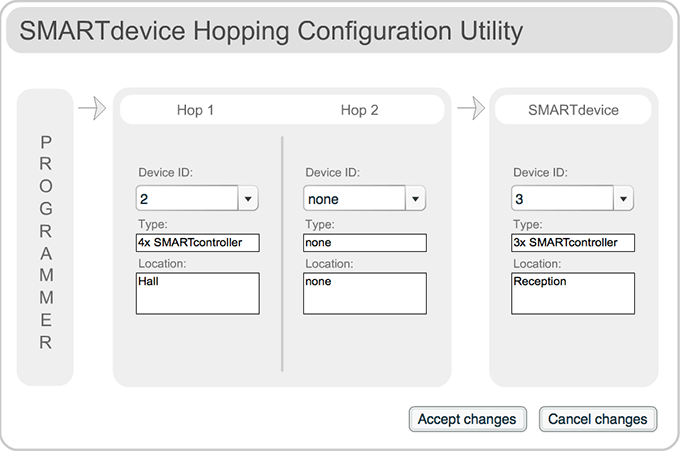
The window is used to hop communications between the WEMSprogrammer and the target device
- Reconnect the battery – this causes the WEMSsensor to 'check in' with the WEMSprogrammer (negating the possible 30 minute wait). Once done the system will keep the communication link alive and then send the hop1 routing instruction.
- Press the button on the WEMSsensor 3–4 times – the red LED will flash rapidly when receiving the hopping instruction.
- Whether the WEMSsensor has taken the new hopping can be tested at this point – if possible, un-power the 'hop1' device and press the button on the WEMSsensor – as 'hop1' is un-powered the WEMSsensor should not gain a green signal test. If it does, the hopping has not been received – disconnect the battery and wait for 1 minute – reconnect and perform 3–4 signal tests to re-initiate a communication link to the WEMSprogrammer.
- To apply hop2 to a WEMSsensor the steps are simply repeated: first disconnect the battery from the WEMSsensor and take it to a location where it will be able to communicate to 'hop1' and 'hop2'.
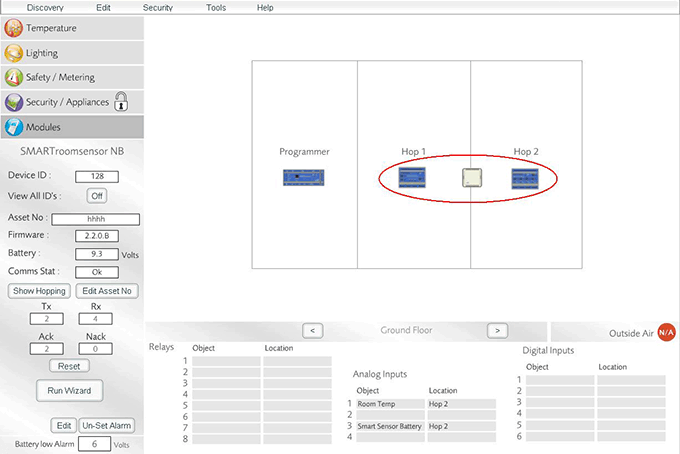
SMARTsensor within communication distance of both hop1 and hop2
- Open the hopping application via the menu and apply your 'hop2' route to the WEMSsensor.
- Reconnect the battery – this causes the WEMSsensor to 'check in' with the WEMSprogrammer (negating the possible 30 minute wait). Once done the system will keep the communication link alive and then send the hop2 routing instruction.
- Press the button on the WEMSsensor 3–4 times – the red LED will flash rapidly when receiving the hopping instruction.
- Whether the WEMSsensor has taken the new hopping can be tested at this point – if possible, un-power the 'hop2' device and press the button on the WEMSsensor – as 'hop2' is un-powered the WEMSsensor should not gain a green signal test. If it does, the hopping has not been received – disconnect the battery and wait for 1 minute – reconnect and perform 3–4 signal tests to re-initiate a communication link to the WEMSprogrammer.